AIR BEARING
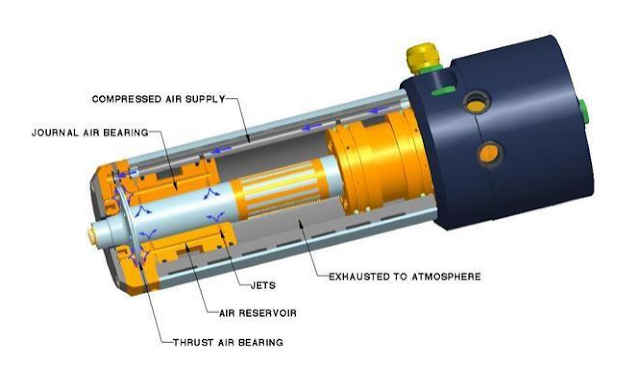
AIR BEARING An air bearing is a non-contacting system where a gas film (usually air) acts as the lubricant that separates the two surfaces in relative motion – typically this being a rotating shaft, and a stationary radial journal or axial thrust bearing. Air bearing vs Ball bearing In the quest for higher productivity, greater accuracy, and longer product life, machine tool and robotic arm OEM’s are constantly pushing the limits of spindle technology fitted to their equipment. Conventional bearing systems, usually ball bearings, cannot always deliver the very high speeds demanded by these industries while still maintaining high rotational precision, thermal stability, and long service life. This is primarily due to the mechanical contact between the balls and the races, which can result in rapid wear and excessive heat generation at high D/N ratios, leading to a loss in accuracy and even premature failure of the bearing. In addition, many advanced industries require oil free bearing