Laser Beam Machining
Laser Beam Machining Definition:
Laser Beam Machining is a non-conventional machining process in which the workpiece is being holed by the laser machining process. To remove the material from the workpiece the process used thermal energy.
Laser Beam Machining Parts or Construction:
Laser Machining consists of the following Main Parts:
- Power Supply
- Capacitor
- Flash Lamps
- Reflecting Mirror
- Laser Light Beam
- Ruby Crystal
- Lens
- Workpiece
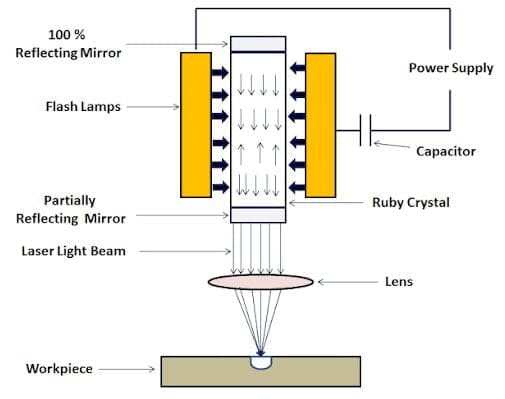
Power Supply:
The electric current or power is supplied to the system. A high voltage power system is used in laser beam machining. It will give initial power to the system after that reaction starts in a laser that will machine the material. There is a high voltage supply so that pulses can be initiated easily
Capacitor:
During the major portion of the cycle, a capacitor bank charges and releases the energy during the flashing process. The capacitor is used for the pulsed mode for charging and discharging.
Flash Lamps:
It is the electric arc lamp that is used to produce extremely intense production of white light which is a coherent high-intensity beam. It is filled with gases that ionize to form great energy that will melt and vaporizes the material of the workpiece.
Reflecting Mirror:
Reflecting Mirror are two main types of internal and external. Internal mirrors also called a resonator that is used to generate maintain and amplify the laser beam. It is used to direct the laser beam towards the workpiece.
Laser Light Beam:
It is the beam of radiation produced by the laser through the process of optical amplification based on the coherence of light created by the bombarding of active material.
Ruby Crystal:
Ruby laser produces a series of coherent pulses which is deep red in color. It achieves by the concept of population inversion. It is a three-level solid-state laser.
Lens:
Lenses are used to focus the laser beam onto the workpiece. First laser light will enter into the expanding lens and then into the collimating lens which makes the light rays parallel and the expanding lens expands the laser beams to the desired size.
Workpiece:
The workpiece can be metallic or non-metallic. In this machining process, any material can be machined.
Laser Beam Machining Working Principle:
Laser Machining is based on the LASER and conversion or process of Electric Energy into Light Energy and into Thermal Energy.
Negatively charged electrons in the atomic model rotate around the positively charged nucleus in orbital paths. It depends on the number of electrons, electron structure, neighboring atoms, and the electromagnetic field.
Every orbital of electrons is associated with different energy levels. An atom is considered to be at ground level at absolute zero temperature at this, all electrons occupy their lowest potential energy.
The electrons at the ground state move to a higher state of energy by absorbing energy like an increase in electronic vibration at elevated temperatures.
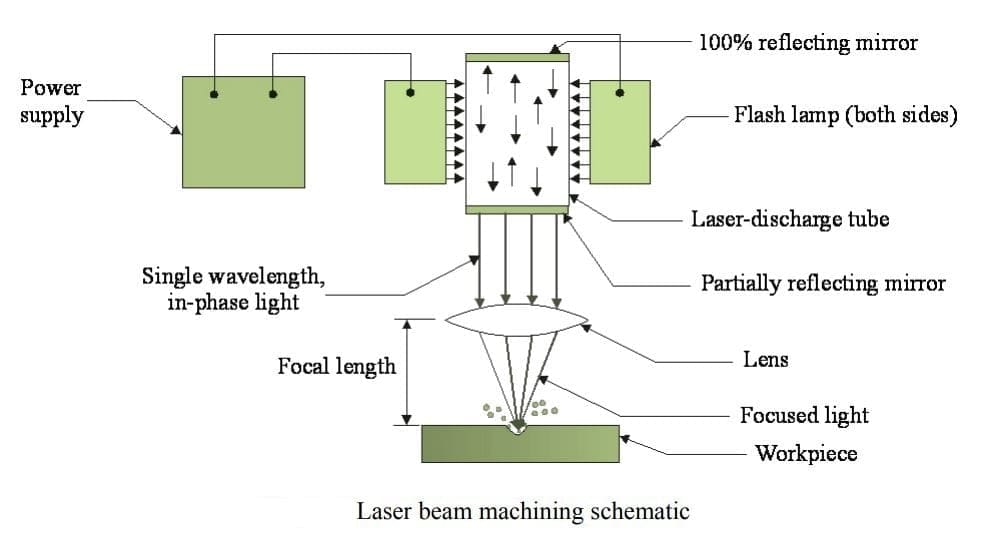
High voltage is applied at the ends that leads to discharge and gas plasma will be formed. Population inversion and lasing action will take takes place due to energy transformation.
The laser has one 100% reflector and the other one is a partial reflector. 100% the reflector directs the photons inside the gas tube and the partial reflector allows only some part of the laser beam that will be used for the processing of materials.
The laser beam produced is focused on the workpiece that has to be machined. When the laser strikes the workpiece, the thermal energy impinges on the workpiece.
This will heat then melt, vaporize, and finally, the material will be removed from the workpiece. So laser machining is a thermal material removal process that uses a coherent beam of light to machine the workpiece very precisely.
In the laser machining process, MRR (Material Removal Rate) depends on the wavelength used because it will decide the amount of energy impinged on it.

Comments