Main Charge Methods for Rechargeable Batteries
Main Charge Methods for Rechargeable Batteries
Constant Current Charging(CC:Constant Current)
Constant current charging is a method of continuously charging a rechargeable battery at a constant current to prevent overcurrent charge conditions.
There is also a method of charging at a low constant current or varying the current in stages to prevent overvoltage charge)
Constant Voltage Charging(CV:Constant Voltage)
Constant voltage charging is a method of charging at a constant voltage to prevent overcharging.
The charging current is initially high then gradually decreases.
There is also a method where the voltage is initially low then gradually increased to prevent excessive temperature rise in the rechargeable battery)
Constant Power Charging(CP:Constant Power)
A constant charging method characterized by high initial current when the voltage is low, then decreasing current as the voltage gradually increases.
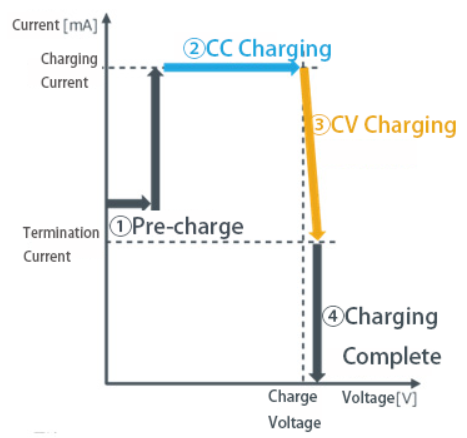
Constant Current Constant Voltage Charging(CCCV:Constant Current , Constant Voltage)
CCCV charging is a typical method of charging rechargeable batteries such as li-ion.
Operation switches between CC charging, which charges with a constant current, and CV that charges at a constant voltage, depending on the voltage of the rechargeable battery.
This is one of the methods used in ROHM charge control ICs.


Comments