Types of Motors used in Electric Vehicles
Types of Motors used in Electric Vehicles
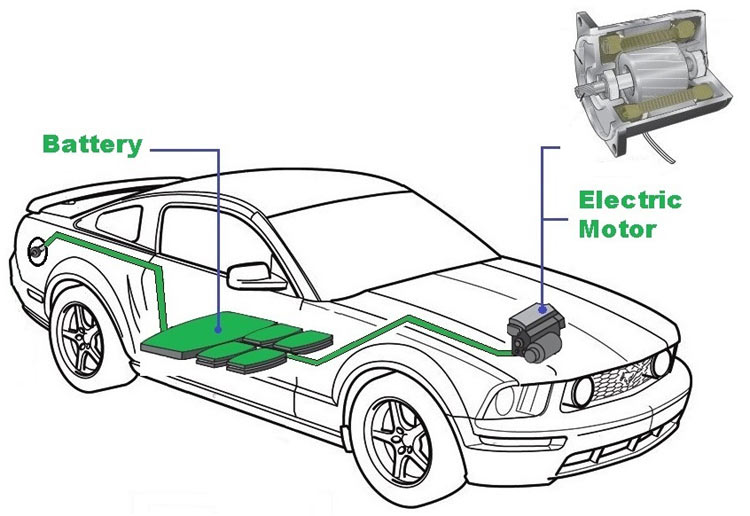
Electric vehicles are not something new to this world, but with the technological advancement and increased concern on controlling pollution has given it a tag of future mobility. The core element of the EV, apart from Electric Vehicle Batteries, which replaces the Internal Combustion engines is an Electric motor. The rapid development in the field of Power electronics and control techniques has created a space for various types of electric motors to be used in Electric Vehicles. The electric motors used for automotive applications should have characteristics like high starting torque, high power density, good efficiency, etc.
Electric motors have become a huge part of our lives. They are found in all sort of devices from electric cars to drones, robots and other Electronics Devices. In general terms, an electric Motor is a device which converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. They are usually referred to as the exact opposite of generators as they operate on similar principles and can theoretically be converted to generators. They are essentially use in situations where rotational motion is needed and they find applications in appliances (vibration motors), robots, medical equipments, toys, and much more.
Electric motors can be categorized into two broad categories based on the kind of power source used for them: AC Motors and DC Motors. As the name implies, AC motors are generically powered using AC power sources(single phase or three phase) and are mostly used in Industrial and heavy duty applications where a lot of torque is required. DC motors (which are our focus for today) on the other hand are usually smaller and are used in battery (or plugged in DC sources) based applications where significantly less amount of work is required compared to AC motors. They find applications in several devices ranging from everyday devices like shaving clippers to toys for kids, robots, and drones among others.
Operation Principle and Construction
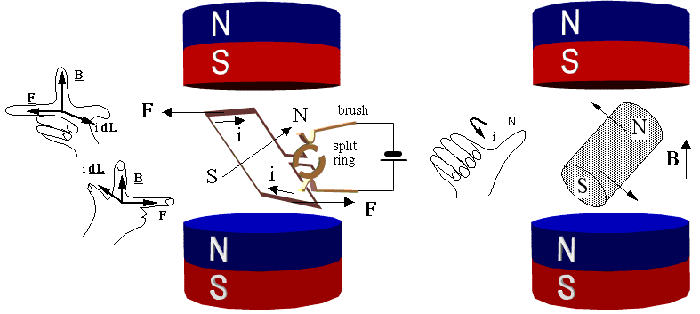
The operation of all motors are generally based on two principles which are; Amperes law and faraday’s law. The first law states that an electrical conductor placed in a magnetic field will experience a force if any current flowing through the conductor has a component at right angles to that field. The second principle states that if a conductor is moved through a magnetic field, then any component of motion perpendicular to that field will generate a potential difference between the ends of the conductor.
Wheel hub motor drive is the most advanced electric vehicle driving technology, which installs two, four or more motors in the wheel, direct driving wheels, commonly known as electric wheels, which is especially suitable for pure electric vehicles.
The external rotor of the motor is mechanically connected with the wheel hub and has no deceleration structure, which is a direct drive mode, see Fig. 4a . Motor speed is generally 1500r/min or so, due to the lack of retarding mechanism, driving structure is compact with high transmission efficiency. But large current is required at the start, climbing or under large loads, which could easily damage the battery and permanent magnets. In order to ensure a large start torque and good dynamic property, the requirements of the motor are high, and low-speed external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor is generally adopted.
Deceleration drive is to installed a fixed speed ratio reducer between the motor and the wheel, playing the role of deceleration and torque-up. The deceleration device is generally a high reduction ratio planetary gear mechanism, see Fig. 4b. The working speed of the motor is about 10000r/min, usually using high-speed inner rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor, the drive wheel hub drives the vehicle after deceleration and torque-up of motor output power. The motor is small, light and with high specific power of high-speed running. After deceleration and torque-up, the vehicle has good climbing ability, and it can guarantee the vehicle has a large steady torque when running at low speed. However, the structure is relatively complex, and the increase of unsprung mass affects the ride comfort and handling stability.






Comments